| Chemical Name: | 4-(chloromethyl)-1H-indazole |
| CAS Number: | 944898-78-6 |
| Product Number: | AG00H6D2(AGN-PC-0ALPV8) |
| Synonyms: | |
| MDL No: | |
| Molecular Formula: | C8H7ClN2 |
| Molecular Weight: | 166.6076 |
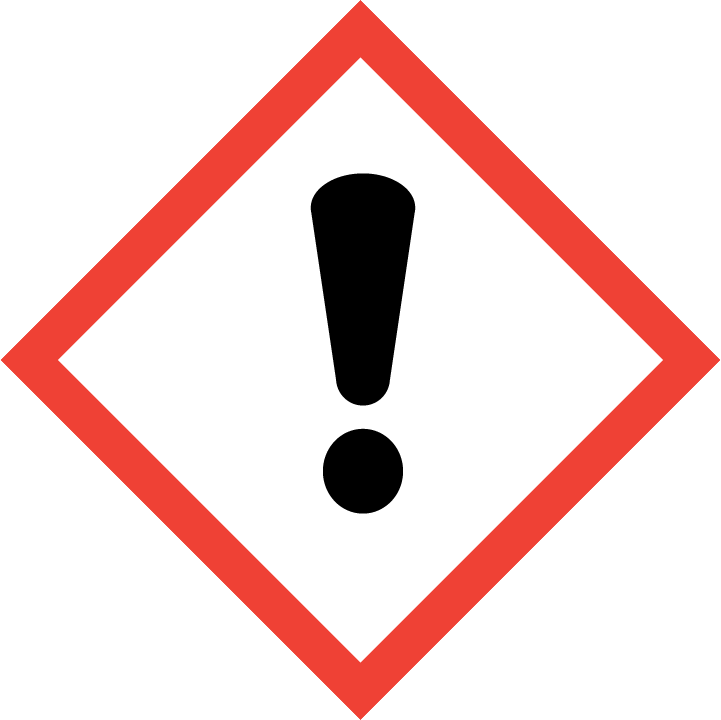

4-(Chloromethyl)-1H-indazole is a versatile compound widely used in chemical synthesis due to its unique reactivity and structural properties. One of the key applications of this compound is in the synthesis of pharmaceutical intermediates, where it serves as a valuable building block for the creation of complex organic molecules. In organic chemistry, 4-(Chloromethyl)-1H-indazole can be utilized in various reactions such as nucleophilic substitution, Suzuki coupling, and Grignard reactions. By incorporating this compound into different synthetic pathways, chemists can access a wide range of structurally diverse compounds with potential biological activities. Additionally, the chloromethyl group in 4-(Chloromethyl)-1H-indazole offers a reactive site for further functionalization, allowing for the introduction of different substituents to tailor the properties of the final products. This flexibility makes it a valuable tool in the design and synthesis of novel compounds for drug discovery and materials science research. Overall, the application of 4-(Chloromethyl)-1H-indazole in chemical synthesis enables chemists to access new molecules and explore the boundaries of organic chemistry, opening up avenues for innovation and discovery in various fields.