| Chemical Name: | (E)-1-(4-isocyanatophenyl)-2-phenyldiazene(SALTDATA |
| CAS Number: | 321951-62-6 |
| Product Number: | AG00C8EK(AGN-PC-0WB5OC) |
| Synonyms: | |
| MDL No: | MFCD00152743 |
| Molecular Formula: | C13H9N3O |
| Molecular Weight: | 223.2301 |
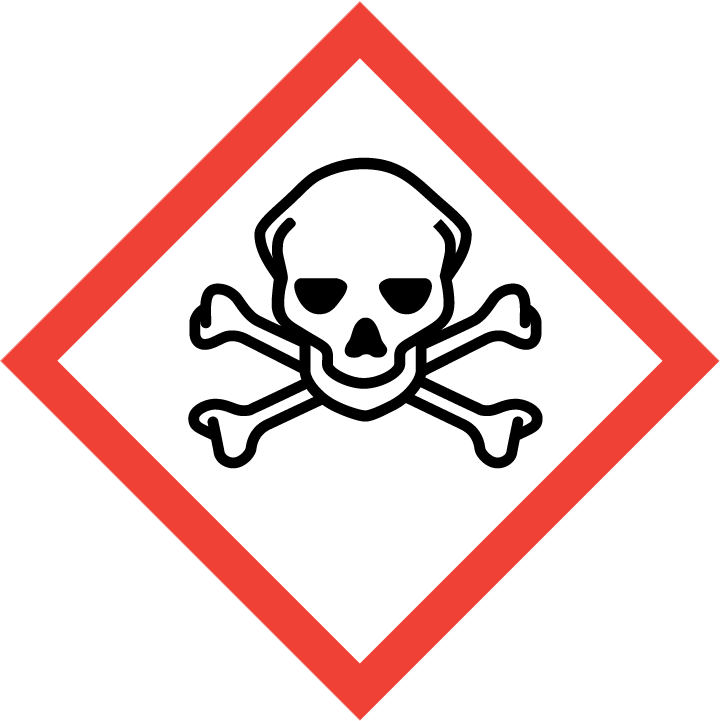
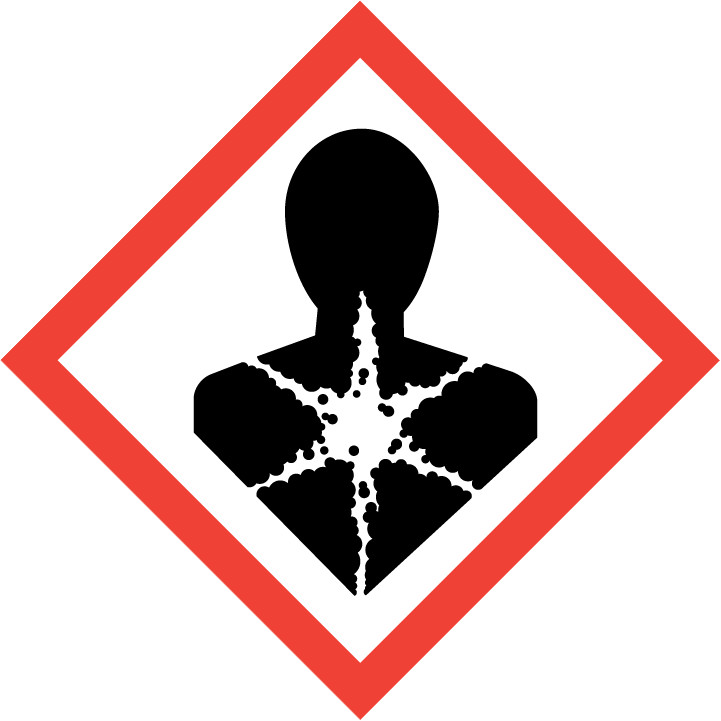


(E)-1-(4-Isocyanatophenyl)-2-phenyldiazene is a versatile compound used in chemical synthesis for its unique properties in catalyzing various reactions. This compound serves as a valuable reagent in organic synthesis, particularly in the formation of azo compounds and as a key intermediate in the preparation of heterocyclic compounds. Its ability to act as a diazene source enables the introduction of the diazenyl functionality into organic molecules, leading to the synthesis of diverse compounds with potential applications in pharmaceuticals, materials science, and agrochemicals. Additionally, (E)-1-(4-Isocyanatophenyl)-2-phenyldiazene is utilized in the development of novel coordination complexes and organometallic compounds, contributing to advancements in the field of inorganic chemistry. This compound plays a crucial role in the creation of complex molecular architectures and serves as a building block for the design of functional materials with tailored properties. By incorporating (E)-1-(4-Isocyanatophenyl)-2-phenyldiazene into synthetic strategies, researchers can access a wide range of chemical transformations, facilitating the discovery of new molecules with enhanced reactivity and potential applications in various scientific disciplines.